Overview
AI-DBA is an exceptional tool that goes beyond just executing recommendations. One of its standout features is its ability to generate comprehensive documentation from the health check data it collects. Let me explain how this process works:
- Data Collection: AI-DBA continuously monitors and analyzes your database, collecting vital health check data. This data includes information about database performance, configuration, security, and more.
- Analysis and Insights: AI-DBA's powerful algorithms process the collected data, identifying potential issues, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. It generates valuable insights based on this analysis.
- Documentation Generation: Based on the insights and analysis, AI-DBA generates detailed documentation that provides a holistic view of your database's health. This documentation includes summaries of the health check data, identified issues, recommended solutions, and best practices.
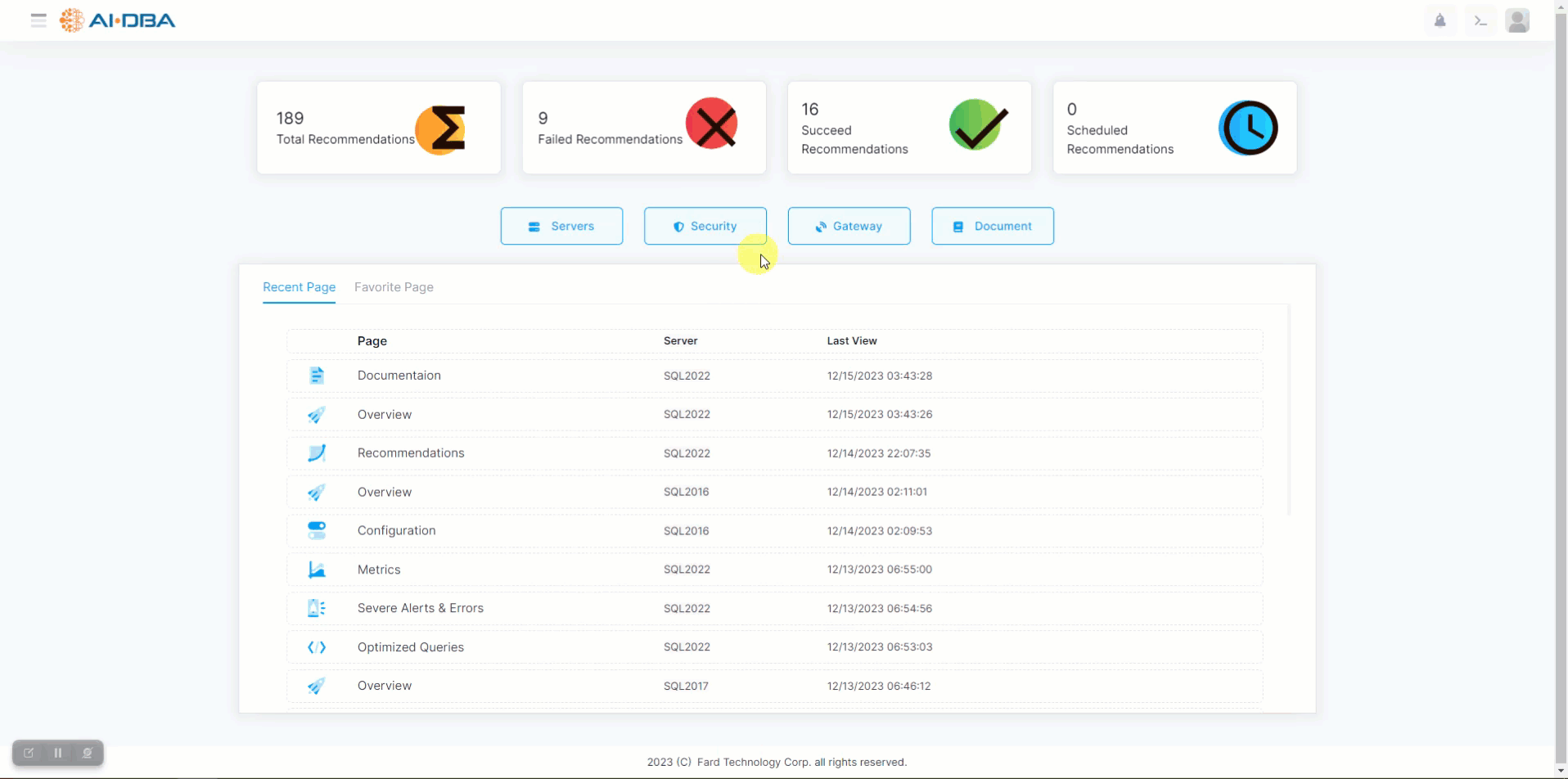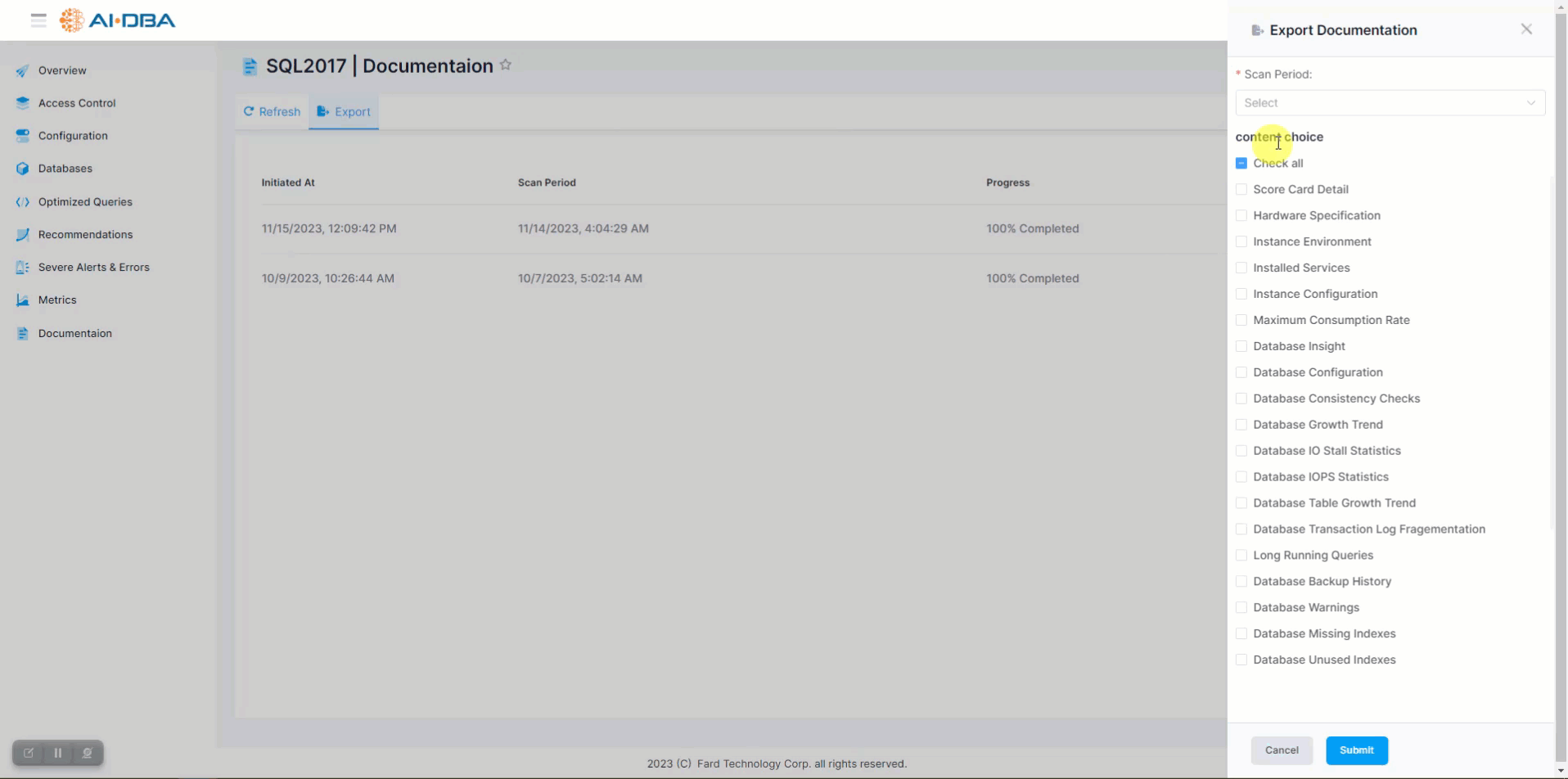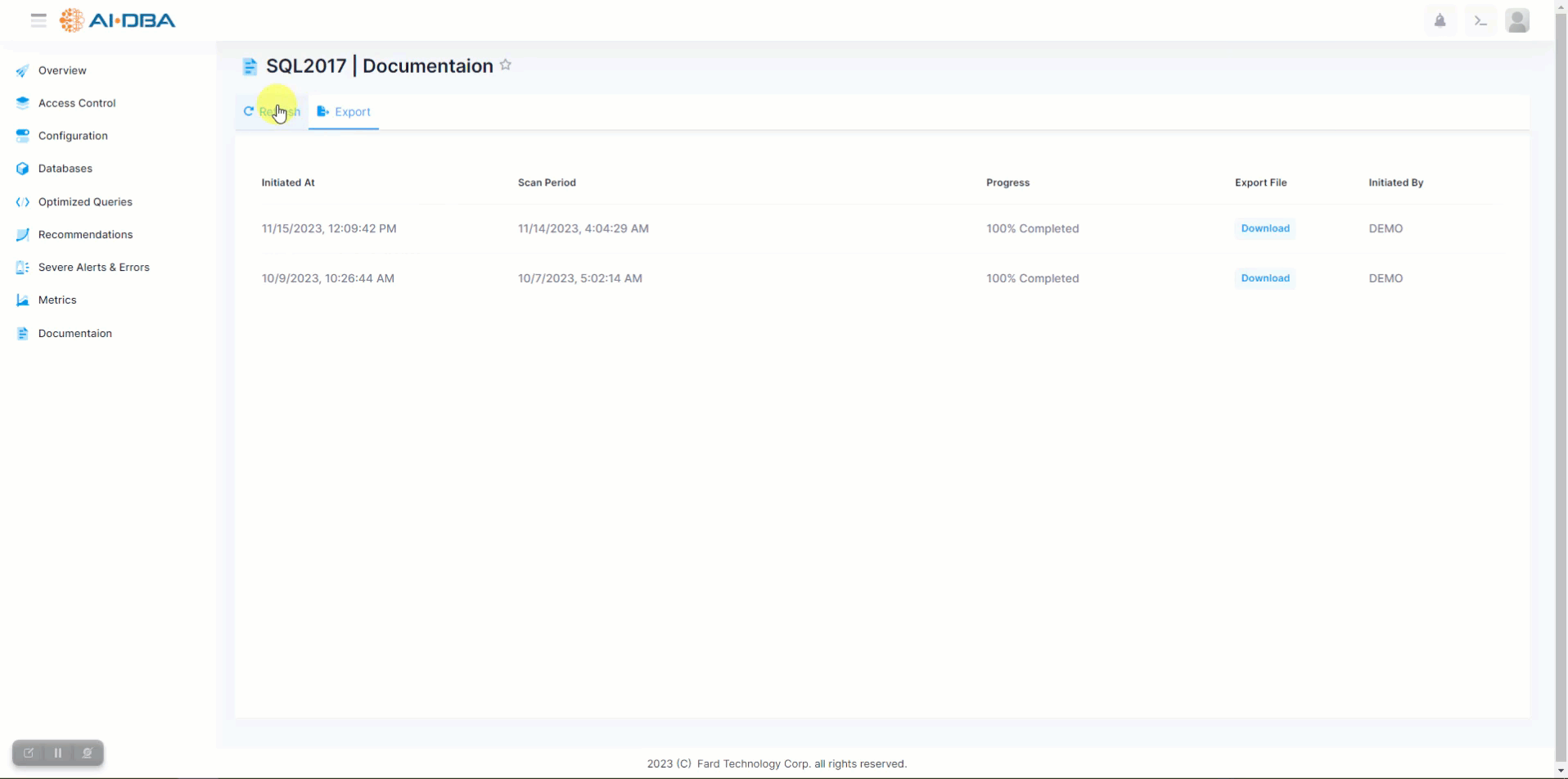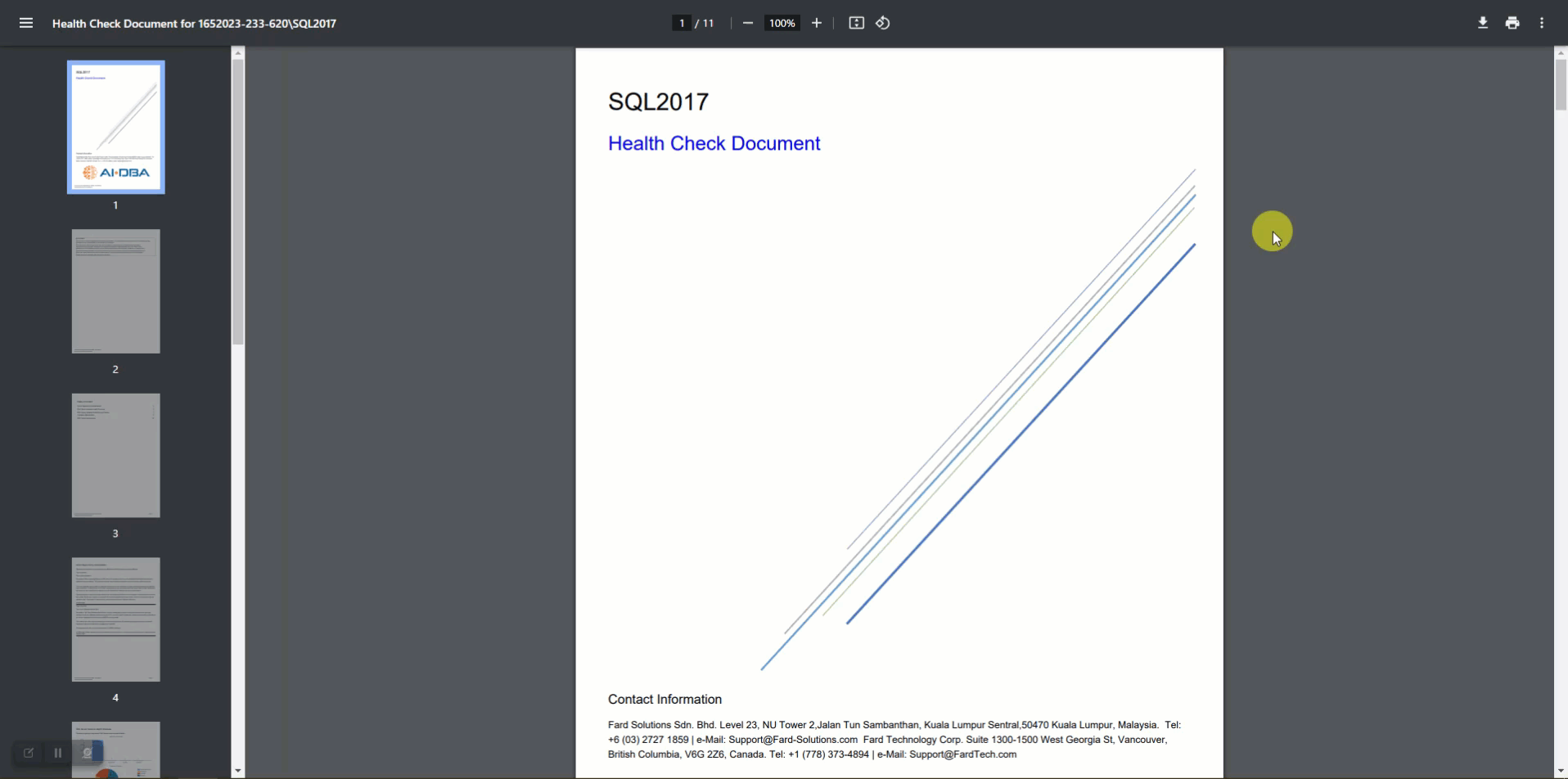
The AI-DBA documentation contains detailed information about various aspects of a database system. Here is a breakdown of the different sections:
- Score Card Detail: This section provides an overview of the overall health and performance of the database system, including metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and disk space.
- Hardware Specification: This section includes information about the hardware components of the server hosting the database, such as the processor, memory, and storage capacity.
- Instance Environment: Here, you can find details about the database instance, including the version of the database software, operating system, and any other relevant environment variables.
- Installed Services: This section lists the services that are installed and running on the database server, such as the database engine, SQL Server Analysis Services, SQL Server Reporting Services, etc.
- Instance Configuration: This section provides information about the configuration settings of the database instance, including memory allocation, parallelism settings, and other instance-level parameters.
- Maximum Consumption Rate: This section shows the maximum rate at which the database system is consuming system resources, such as CPU, memory, and disk I/O.
- Database Insight: Here, you can find insights and statistics about the database, such as the total number of tables, indexes, and stored procedures, as well as the size of the database.
- Database Configuration: This section provides details about the configuration settings of the database, including file locations, autogrowth settings, and other database-level parameters.
- Database Consistency Checks: This section shows the results of consistency checks performed on the database, such as checking for data corruption or integrity issues.
- Database Growth Trend: Here, you can find information about the growth trend of the database, including the rate at which the database size is increasing over time.
- Database IO Stall Statistics: This section provides statistics about IO stalls, which indicate delays in reading or writing data from/to disk.
- Database IOPS Statistics: Here, you can find statistics about the Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS) performed by the database system.
- Database Table Growth Trend: This section shows the growth trend of individual tables in the database, including the rate at which their size is increasing over time.
- Database Transaction Log Fragmentation: Here, you can find information about the fragmentation level of the transaction log, which can impact performance.
- Long Running Queries: This section lists the queries that have been running for an extended period of time, which could indicate performance issues.
- Database Backup History: Here, you can find the history of database backups, including the backup type, date, and size.
- Database Warnings: This section lists any warnings or advisory messages generated by the database system.
- Database Missing Indexes: Here, you can find information about any missing indexes that could improve query performance.
- Database Unused Indexes: This section lists any indexes that are not being used by the database system and could potentially be removed.
- Login and Credentials: Here, you can find information about the logins and credentials used to access the database.
- Linked Servers: This section provides details about any linked servers configured in the database system.
- SQL Agent Alerts and Jobs: Here, you can find information about any alerts and jobs configured in the SQL Server Agent.
- SQL Agent Job History: This section shows the history of SQL Agent job executions, including the start time, end time, and status.
- Severe Alerts and Errors: This section lists any severe alerts or errors generated by the database system.
- Recommendations: Here, you can find recommendations for optimizing the performance and stability of the database system.
- Query Performance Comparison: This section compares the performance of different queries, allowing you to identify bottlenecks and optimize query execution.
Overall, the AI-DBA documentation provides a comprehensive overview of the database system, helping administrators and developers monitor and optimize.